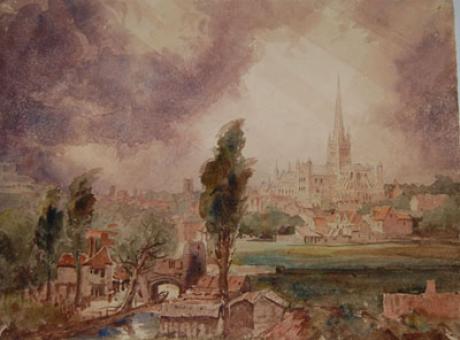"Jun 15 - 1855"
The structure of the cathedral is primarily in the Norman style, having been constructed at the behest of Bishop Herbert de Losinga between the late 11th century and about 1145. The total length of the building is 461 feet (140 m). Significant alterations from later periods include a 315 foot (96 m) spire completed in 1465, and a two-storey cloister, the only such in England, which was built between 1300 and 1430, as well as the vaults of nave and chancel. The cathedral is built of flint and mortar faced with limestone brought in from Caen. Standing at 315 feet, the cathedral's spire is the second tallest in England, and dominates the city skyline; only the spire of Salisbury Cathedral is higher at 404 feet. Along with Salisbury and Ely, the cathedral lacks a ring of bells - the only three English cathedrals to do so. One of the best views of the cathedral spire is from St. James's Hill on Mousehold Heath. The bosses of the vault number over 1,000. Each is decorated with a theological image and have been described as without parallel in the Christian world. The nave vault shows the history of the world from the creation; the cloister includes series showing the life of Christ, and the Apocalypse.
The precinct of the cathedral, the limit of the former monastery, is between Tombland (the Anglo-Saxon market place) and the River Wensum - building materials were taken up the Wensum and unloaded at Pulls Ferry, Norwich. The Cathedral Close, which runs from Tombland into the cathedral grounds, contains a number of interesting buildings from the 15th through to the 19th century, including the remains of the Infirmary. The grounds also house the King Edward VI school, statues to the Duke of Wellington and Admiral Nelson and the grave of Edith Cavell. The cathedral was partially in ruins when John Cosin was there at Grammar School in the early 1600s, and the former bishop was an absentee figure. During the reign of King Charles I, an angry Puritan mob invaded the cathedral and destroyed all Catholic symbols in 1643. The building, abandoned the following year, lay in ruins for two decades. Norwich Bishop Joseph Hall provides a graphic description from his book Hard Measure:
It is tragical to relate the furious sacrilege committed under the authority of Linsey, Tofts the sheriff, and Greenwood: what clattering of glasses, what beating down of walls, what tearing down of monuments, what pulling down of seats, and wresting out of irons and brass from the windows and graves; what defacing of arms, what demolishing of curious stone-work, that had not any representation in the world but of the cost of the founder and skill of the mason; what piping on the destroyed organ-pipes; vestments, both copes and surplices, together with the leaden cross which had been newly sawed down from over the greenyard pulpit, and the singing-books and service-books, were carried to the fire in the public market-place; a lewd wretch walking before the train in his cope trailing in the dirt, with a service-book in his hand, imitating in an impious scorn the tune, and usurping the words of the litany. The ordnance being discharged on the guild-day, the cathedral was filled with musketeers, drinking and tobacconing as freely as if it had turned ale-house. Only at the Restoration in 1660 would the cathedral be restored under Charles II.
The Rev John Louis Petit (1801–1868), architectural historian and watercolour painter, was born on 31 May 1801 in Ashton under Lyne, Lancashire, the only son of John Hayes Petit (1771–1822), a Church of England clergyman and JP, and his wife, Harriet Astley.
The family was descended from Lewis Petit, also known as Lewis Petit des Etans (1665?–1720), a Huguenot refugee and military engineer. Petit's grandfather was John Lewis Petit (1736–1780), the son of John Petit of Little Aston Hall, Shenstone, Staffordshire. He graduated from Queens' College, Cambridge (BA 1756, MA 1759, and MD 1766), was elected fellow of the College of Physicians in 1767, was Gulstonian lecturer in 1768, and was censor in that year, 1774, and 1777. From 1770 to 1774 he was physician to St George's Hospital, then on the death of Dr Anthony Askew in 1774 he was elected physician to St Bartholomew's Hospital. In November 1769 he married Katherine Laetitia Serces, the daughter of one of the preachers of the French Chapel Royal in London. He died on 27 May 1780 and was buried at St Anne's, Soho. John Louis Petit was educated at Eton College and contributed to The Etonian, then in its heyday. He was elected to a scholarship at Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1822, and graduated BA in 1823 and MA in 1826. On 17 June 1828 he married Louisa Elizabeth, the daughter of George Reid of Trelawny, Jamaica. He had been ordained deacon in 1824 and priest the year after, but it was not until 1840 that he took up his sole church appointment, as curate of Bradfield in Essex, which he held until 1848. By this time he had written and illustrated several works of architectural history, the main occupation of his career.
Petit had shown a taste for sketching in his early years and he made many hundreds of drawings in pencil and ink. These were often finished in watercolour, though in a limited palette. His favourite subject was old buildings, particularly churches, and he spent much time visiting and sketching them. His drawings were rapidly and adeptly executed on the spot, his style in the tradition of English topographical watercolour painters of the previous generation, such as Samuel Prout (1783–1852). Although his works display an instinct for the picturesque setting and the telling viewpoint, his aim was less to produce finished paintings for their own sake than to record historic buildings and architectural details. Many were reproduced in his profusely illustrated books. He occasionally painted in oils. In almost all of these respects he resembles John Ruskin (1819–1900), whose concern for the conservation of old buildings was Petit's too. In 1839 Petit made his first extensive tour on the continent, which informed his Remarks on Church Architecture (1841), part travelogue, part discursive survey of architectural styles since the Roman. Subsequent works provide more detailed analyses of individual buildings, including Tewkesbury Abbey, Sherborne Abbey, and Southwell Minster. Petit's credentials as an antiquary are reflected in his co-founding of the British Archaeological Institute in 1844 and his elections as fellow of the Society of Antiquaries and honorary member of the Institute of British Architects. He lectured to the Oxford society for promoting the study of Gothic architecture, a body which mirrored the Cambridge Camden Society and whose membership similarly took a deep interest in the way churches old and new should be laid out and used. This Oxford connection was fruitful academically for Petit, who was admitted to the university ad eundem in 1850, and personally too, as his sister, Maria, married a classics don, William Jelf (1811–1875), in 1849. Architectural Studies in France, Petit's principal work, appeared in 1854 (new edition 1890). It is a detailed survey of French Gothic, profusely illustrated by Petit and by his companion on the research tour, Philip Delamotte (1820/21–1889), an artist, engraver, and early exponent of photography. Petit does not seem to have used photography for recording buildings; nevertheless, some of the illustrations were reproduced using a new technique, that of anastatic drawing.
Petit's books come from a rich period in England for research, publication, and debate on architectural history. His writing style was accessible and the illustrations attractive, but he lacked the intellectual rigour of others in the field, such as his Cambridge contemporaries William Whewell (1794–1866) and Robert Willis (1800–1875). His judgements could be shaky and, with his genteel admiration of almost anything old, he could elicit harsh reviews at a time when attitudes were hardening in favour of particular styles as models for revival. While he had a taste for the Romanesque, for example, just before it became fashionable as a style for new churches in the 1840s, he did not make himself its champion. He was not a polemicist like A. W. N. Pugin or George Gilbert Scott; besides, he had a distaste for debates that smacked of religious controversy. This was the tendency from the 1840s, particularly in the pages of The Ecclesiologist, the organ of the Cambridge Camden Society.
When Petit did turn his attention to contemporary architectural practice, he encountered spirited opposition. In 1841 Scott's designs for the remodelling of St Mary's, Stafford, were exhibited. This was a church close to Petit's heart (his brother-in-law was a benefactor) and he objected in writing to the proposal for the thoroughgoing redesign of the south transept. He could accept Scott's interventions elsewhere in the building but not so the replacement of Gothic fabric, albeit sixteenth-century. Scott accepted the principle but argued that it could be ignored if the style was ‘debased’. Their debate by correspondence was eventually put to a panel of experts from the Cambridge Camden Society and the Oxford society noted above. Scott won and Petit gamely published the papers. As galling was the reception of Petit's only executed architectural design. His sister and brother-in-law moved to Cae'rdeon, near Barmouth, Merioneth, in 1854. Jelf took exception to the fact that most of the services in the Anglican parish church were said in Welsh, so in 1862 he asked his brother-in-law to design him a church, to be built at his own expense, where he could officiate in English. Petit designed him a rugged and muscular church for the mountainous setting. The Ecclesiologist lambasted it in a pithy review, attacking the design on practical grounds (roof pitches too shallow) and on theoretical grounds (pilasters for show, not structural necessity). The critic is clearly exasperated that Petit preferred picturesque effect to the application of formal principles: the alpine-style stone hut is simply not appropriate for an Anglican church on a turnpike road. There may also be a difference of churchmanship here. Petit and Jelf (for all his belligerence on the language issue) had avoided the febrile excesses of the Oxford Movement. Happily, St Philip Cae'rdeon still stands, somewhat altered but recently repaired.
During 1864–5 Petit travelled to Syria, Palestine, and Egypt. He continued to draw and paint avidly. He died in Lichfield on 1 December 1868 from a cold caught or aggravated while out sketching, and was buried in St Michael's churchyard. An exhibition of 339 of his sketches, including two views of the church at Cae'rdeon, was shown by the Architectural Exhibition Society in London during 1869. That year also saw the posthumous publication of a volume of his poetry. Sir Nikolaus Pevsner gives a characteristically pungent account of Petit in his survey of nineteenth-century architectural writers. As an artist, his modest talent was given almost unlimited scope, producing a corpus of architectural impressions which is impressive, if slight as individual works of art. As a critic of contemporary practice, he is probably most significant as a spokesman for tolerance: he valued buildings and styles of many eras and favoured, if not consistently or dogmatically, repair over rebuilding.