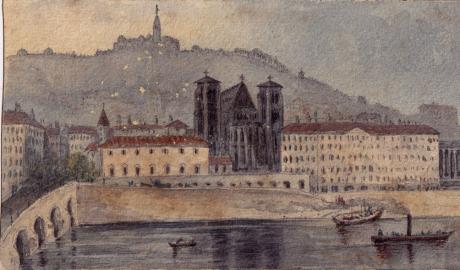inscribed signed with monogram and dated on the reverse " Lyons E.T.L. 1874"
Lyon Cathedral (French: Cathédrale Saint-Jean-Baptiste de Lyon) is a Roman Catholic church located on Place Saint-Jean in central Lyon, France. The cathedral is dedicated to Saint John the Baptist, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Lyon.
The cathedral was founded by Saint Pothinus and Saint Irenaeus, the first two bishops of Lyon. The cathedral is also known as a "Primatiale" because in 1079 the Pope granted to the archbishop of Lyon the title of Primate of All the Gauls with the legal supremacy over the principal archbishops of the kingdom. It is located in the heart of the old town (Vieux Lyon) and it backs up to the Saône river, with a large plaza in front of it and a metro stop nearby providing easy access to and from the city center.
Patiens of Lyon, who was bishop around 450 AD, built a new cathedral, dedicated to Saint Stephen. Later, in the seventh century, a baptistery dedicated to Saint John was constructed as an accessory building to the church. The Church of St. Croix was also near. This location later became the site of the Cathédrale Saint-Jean-Baptiste.
In 1245, the cathedral hosted the First Council of Lyon.
In 1819 J. M. W. Turner sketched a study of the Cathedral as seen from the heights of the Fourvière Hill. Edgar Degas used the cathedral for the setting of his painting "Ceremony of Ordination at Lyon Cathedral."
Each December, Lyon holds an annual Festival of Lights. The tradition dates to 1643, when on 8 December the people of Lyon would place a lit candle in the window, a custom still maintained by many residents to this day. During the Festival, a choreographed lighting display appears on the façade of the cathedral.
Description
Begun in 1180 on the ruins of a 6th-century church, it was completed in 1476. The building is 80 meters long (internally), 20 meters wide at the choir, and 32.5 meters high in the nave. The apse and choir are of Romanesque design; the nave and façade are Gothic.
Noteworthy are the two crosses to right and left of the altar, preserved since the Second Council of Lyon of 1274 as a symbol of the union of the churches, and the Bourbon chapel, built by the Cardinal Charles II, Duke of Bourbon and his brother Pierre de Bourbon, son-in-law of Louis XI, a masterpiece of 15th century sculpture.
The cathedral also has the Lyon Astronomical Clock from the 14th century.
The cathedral organ was built by Daublaine and Callinet and was installed in 1841 at the end of the apse and had 15 stops. It was rebuilt in 1875 by Merklin-Schütze and given 30 stops, three keyboards of 54 notes and pedals for 27. Until the construction of the Basilica of Notre-Dame de Fourvière, it was the pre-eminent church in Lyon. Renowned organist Edouard Commette served as the resident organist for most of the first half of the 20th century.
Lyon or Lyons is the third-largest city and second-largest urban area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, about 470 km (292 mi) southeast of Paris, 320 km (199 mi) north of Marseille and 56 km (35 mi) northeast of Saint-Étienne. Inhabitants of the city are called Lyonnais (masculine) and Lyonnaises (feminine).
The City of Lyon proper had a population of 516,092 in 2017 within its small municipal territory of 48 km2 (19 sq mi), but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Lyon metropolitan area had a population of 2,323,221 that same year, the second-most populated in France. The City of Lyon and 58 suburban municipalities have formed since 2015 the Metropolis of Lyon, a directly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of most urban issues, with a population of 1,385,927 in 2017. Lyon is the prefecture of the region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes as well as the seat of the Rhône Departmental Council (whose jurisdiction, however, no longer extends over the Metropolis of Lyon since 2015).
Former capital of the Gauls at the time of the Roman Empire, Lyon is the seat of an archbishopric whose holder bears the title of Primate of the Gauls. Lyon became a major economic hub during the Renaissance. The city is recognised for its cuisine and gastronomy, as well as historical and architectural landmarks; as such, the districts of Old Lyon, the Fourvière hill, the Presqu'île and the slopes of the Croix-Rousse are inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List. Lyon was historically an important area for the production and weaving of silk. Lyon played a significant role in the history of cinema: it is where Auguste and Louis Lumière invented the cinematograph. It is also known for its light festival, the Fête des Lumières, which begins every 8 December and lasts for four days, earning Lyon the title of "Capital of Lights".
Economically, Lyon is a major centre for banking, as well as for the chemical, pharmaceutical and biotech industries. The city contains a significant software industry with a particular focus on video games; in recent years it has fostered a growing local start-up sector. Lyon hosts the international headquarters of Interpol, the International Agency for Research on Cancer and Euronews. According to the Globalization and World Rankings Research Institute, Lyon is considered a Beta city, as of 2018. It ranked second in France and 40th globally in Mercer's 2019 liveability rankings.
Fernand Braudel remarked, "Historians of Lyon are not sufficiently aware of the bi-polarity between Paris and Lyon, which is a constant structure in French development...from the late Middle Ages to the Industrial Revolution". In the late 15th century, the fairs introduced by Italian merchants made Lyon the economic counting house of France. Even the Bourse (treasury), built in 1749, resembled a public bazaar where accounts were settled in the open air. When international banking moved to Genoa, then Amsterdam, Lyon remained the banking centre of France.
During the Renaissance, the city's development was driven by the silk trade, which strengthened its ties to Italy. Italian influence on Lyon's architecture is still visible among historic buildings. In the late 1400s and 1500s Lyon was also a key centre of literary activity and book publishing, both of French writers (such as Maurice Scève, Antoine Heroet, and Louise Labé) and of Italians in exile (such as Luigi Alamanni and Gian Giorgio Trissino).
In 1572, Lyon was a scene of mass violence by Catholics against Protestant Huguenots in the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre. Two centuries later, Lyon was again convulsed by violence during the French Revolution, when the citizenry rose up against the National Convention and supported the Girondins. The city was besieged by Revolutionary armies for over two months before it surrendered in October 1793. Many buildings were destroyed, especially around the Place Bellecour, and Jean-Marie Collot d'Herbois and Joseph Fouché administered the execution of more than 2,000 people. The Convention ordered that its name be changed to "Liberated City", and a plaque was erected that proclaimed "Lyons made war on Liberty; Lyons no longer exists". A decade later, Napoleon ordered the reconstruction of all the buildings demolished during that period.
The Convention was not the only target within Lyon during the French Revolution. After the Convention faded into history, the French Directory appeared and days after the September 4, 1797 Coup of 18 Fructidor, a Directory's commissioner was assassinated in Lyon. The city became an important industrial town in the 19th century. In 1831 and 1834, the canuts (silk workers) of Lyon staged two major uprisings for better working conditions and pay. In 1862, the first of Lyon's extensive network of funicular railways began operation. During World War II, Lyon was a centre for the occupying Nazi forces, including Klaus Barbie, the infamous "Butcher of Lyon". However, the city was also a stronghold of the French Resistance, the many secret passages known as traboules, enabled people to escape Gestapo raids. On 3 September 1944, Lyon was liberated by the 1st Free French Division and the Forces Françaises de l'Intérieur. The city is now home to a Resistance museum.